Building Block Is The Monosaccharide
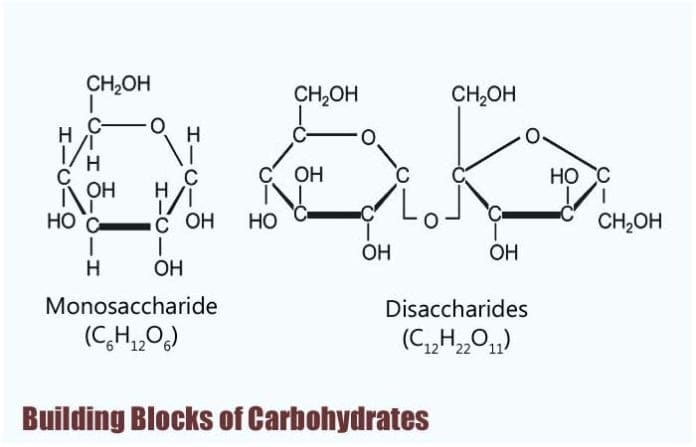
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates: The bones biochemistry of living organisms tin can, therefore, exist understood regarding the morphology and physiology of the iv biological macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Among these 4 macromolecules, carbohydrates are considered to be the nigh abundant as they serve equally the firsthand sources of free energy of living organisms.
The give-and-take "carbohydrate" comes from the two Greek words "carbo" and "hydro" which mean "carbon" or "coal" and "h2o" respectively. This probably came to the fact that when sugars are heated, carbon and water are released. In biochemical terms, they are referred to every bit either polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones.
But what exactly make up these circuitous macromolecules tha e them to carry out such functions? In this article, allow'south explore about these carbohydrates and their biological edifice blocks: the monosaccharides.
Table of Contents
- Building Blocks of Carbohydrates
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides
- Three Most Common Monosaccharides
- 1. Glucose
- 2. Fructose
- 3. Galactose
- The Glycosidic Bond
- Polysaccharides
- i. Glycogen
- 2. Starch
- Office of Carbohydrates
- References
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates
Concrete and Chemical Properties of Monosaccharides
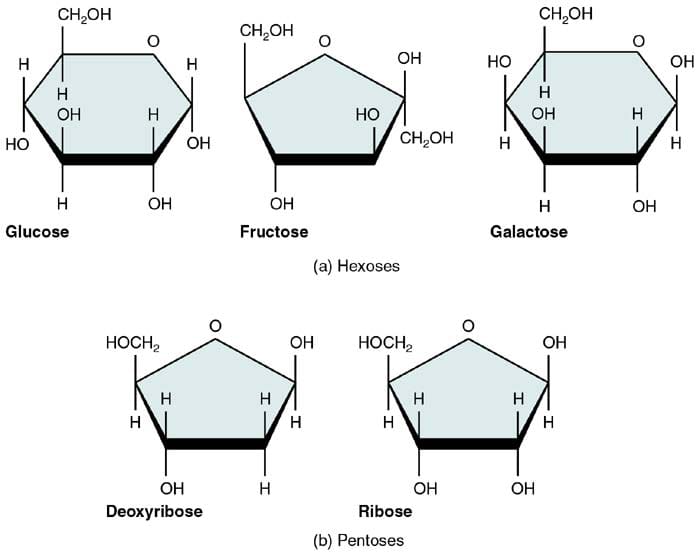
Monosaccharides are known to be the simplest form of carbohydrates, and every bit such, they are considered to exist their edifice blocks.
The term "monosaccharide" comes from the Greek word "mono" which means "one" and "saccharide" which ways "sugar" or "sweetness."
This is considering monosaccharides contain simply one unit of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone and are grouped according to the number of carbon they have.
- In general, monosaccharides, share the aforementioned chemic formula of C6H12O6, and because having half-dozen carbon atoms, they are also called as hexose.
- Being sugars, monosaccharides naturally have a sweet taste (fructose is considered to be the sweetest among them) and remain in their solid forms at room temperature.
- In spite of their very high molecular weights, they are very soluble in water as compared with other substances with the aforementioned molecular weight. The fact that there are a lot of OH groups in their structure makes this possible.
- Regarding their chemical composition, monosaccharides do not usually exhibit their open-chain structures. In this type of formation, an booze group can be readily added to the carbonyl grouping to create a pyranose ring that contains a stable conformation of a cyclic hemiacetal or hemiketal.
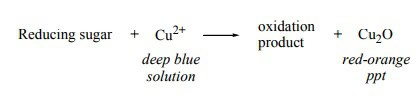
Monosaccharides, in general, can be readily oxidized by certain chemicals. The aldehydes and ketones in their structures incorporate OH groups located on the carbon next to the carbonyl group that can react with the cupric ions (Cu) of Benedict's reagent. Later this reaction, a formation of an orangish precipitate of copper (I) oxide or CuiiO will occur.
All monosaccharides undergo this type of reaction and are called reducing sugars. (The chemic reaction is shown to a higher place)
![]()
Three Most Mutual Monosaccharides
There are three most mutual naturally occurring monosaccharides: glucose, fructose, and galactose. Despite sharing the aforementioned chemical formula, they have dissimilar structural configurations, thus making them different regarding overall structure and function.
i. Glucose

Considered as the most disquisitional monosaccharide, glucose is likewise known every bit dextrose or blood sugar. As it is, it serves as an firsthand energy source during cellular respiration (photosynthesis).
- Glucose is naturally occurring in plants and animals in its free form. Information technology is synthesized in a process chosen gluconeogenesis from non-carbohydrate molecules like glycerol and pyruvate. At the aforementioned time, information technology can too come up from the pause-down of glycogen in the process called glycogenolysis.
![]()
two. Fructose

Also known as fruit sugar, fructose is the natural sugar that is found in fruits and dear. Overall, it is considered to be the sweetest amid sugars. In chemical terms, fructose is also called equally levulose.
- Intendance should be taken when consuming likewise much fructose as it is often associated with gastrointestinal problems and with somehow contributes to the increase in the fat content of blood.
![]()
3. Galactose

Last merely not the least is the monosaccharide galactose that is derived from the hydrolysis of the disaccharide lactose (milk-carbohydrate). This lactose derived from milk is an essential energy source for many animals, including humans.
- Interestingly, the mammalian torso can catechumen glucose to galactose for the mammary glands to produce the lactose in milk.
![]()
The Glycosidic Bond
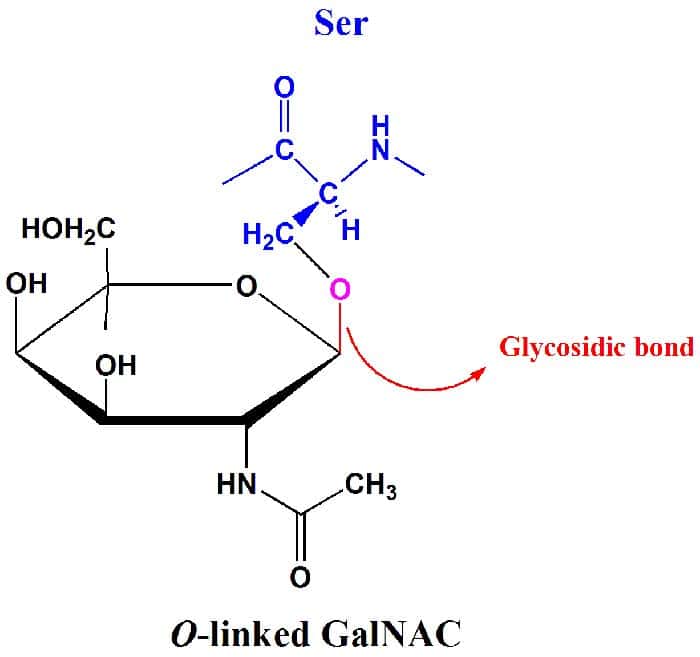
Because monosaccharides (and other carbohydrates) have many OH groups, they can be joined to i another by covalent bonds. In particular, glycosidic bonds are the blazon of covalent bonds that bring together together sugar molecules with other groups, which may or may not be of the same type.
- As their proper noun suggests, they are involved with glycosides which are band-shaped carbohydrate molecules that may either be a five-membered ring or a vi-membered one.
- It should as well be of import to note that not all glycosidic bonds are the same: they can be either linked to a nitrogen or oxygen.
And just like what was alluded to above, the fact that monosaccharides contain many OH groups ways that many linkages via glycosidic bonds are possible. Hence, the variety of these ties tin be correlated with the vast array of monosaccharides, and their forms make more than complex carbohydrates exist packed with much information.
![]()
Polysaccharides

Long chains of polymeric saccharides that are formedvia the glycosidic linkages of monosaccharides are known equally polysaccharides. Being circuitous sugars, they play essential roles in the maintenance of an organism's structural integrity too as the storage of energy.
- Polysaccharides that are made up of the same type of monosaccharides are referred to as homopolymers.
- There are two most common types of polysaccharides in animate being and plant cells: glycogen and starch. They are described below.
![]()
1. Glycogen

In animals, the most mutual blazon of homopolymer is glycogen. Glycogen is a very big polysaccharide fabricated of glucose monomers and is considered to exist the storage course of carbohydrates in fauna cells.
- Its glucose units are generally linked via α-1,4-glycosidic bonds; however, at nigh every x units, linkages via α-i,6-glycosidic bonds are used.
![]()
two. Starch

On the other paw, starch is the storage form of energy in plants. It comes in two forms: amylose and amylopectin. These two types are readily hydrolyzed past the enzyme (called α-amylase) produced by the salivary glands in the rima oris and by the pancreas.
- Amylose is the unbranched type and is composed of glucose units linked via α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. Reverse, amylopectin is the branched type and is connected via α-1,vi glycosidic bonds, in the same way, that glycogen is formed.
Nevertheless, you don't ever need many monosaccharide units to grade a polysaccharide. A special type of polysaccharide, called a disaccharide, is fabricated upwards of just ii monosaccharide units linked via a glycosidic bail. The most common disaccharides are sucrose (glucose and fructose), lactose (glucose and galactose), and maltose (two glucose).
![]()
Function of Carbohydrates
Equally alluded to earlier, carbohydrates serve as the firsthand energy sources. In higher organisms, they serve to enable the metabolism of fats to avoid the breaking down of proteins for energy. Bated from that carbohydrates are also needed to metabolize fats. Apparently, if the body generates enough energy for its physiological functions, actress energy becomes stored as fat.
![]()
In conclusion, monosaccharide as carbohydrate building blocks can exist linked to a wide variety of stereochemistries which are essential in the germination of more complex structures. Because of these small units, living organisms are supplied with ample corporeality of free energy that helps them survive. Indeed, pocket-sized things make a big difference.
![]()
Cite This Page
References
- "Saccharide definition and meaning | Collins English language Lexicon". Accessed November 21, 2017. Link.
- "Circuitous Carbohydrates Are Formed by Linkage of Monosaccharides – Biochemistry – NCBI Bookshelf". Accessed Nov 21, 2017. Link.
- "Nutrient Tests – Benedict's Examination for Reducing Sugar – Brilliant Biology Student". Accessed November 21, 2017. Link.
- "Glycogenolysis and glycogenesis – Metabolism, insulin and other hormones – Diapedia, The Living Textbook of Diabetes". Accessed November 21, 2017. Link.
- "Fructose is generated in the human encephalon | YaleNews". Accessed Nov 21, 2017. Link.
- "Open up Learning Initiative: Register for a Course". Accessed November 21, 2017. Link.
- "Glycogen Biosynthesis; Glycogen Breakup". Accessed Nov 21, 2017. Link.
- "PDB-101: Alpha-amylase". Accessed November 21, 2017. Link.
Building Block Is The Monosaccharide,
Source: https://www.bioexplorer.net/building-blocks-of-carbohydrates.html/#:~:text=Monosaccharides%20are%20known%20to%20be,to%20be%20their%20building%20blocks.
Posted by: kleinmese1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Building Block Is The Monosaccharide"
Post a Comment